What is Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software?

To define that, what is customer relationship management CRM software? We can say it is the combination of practices, strategies, and technologies which companies use to manage and evaluate customer experiences and data across the customer lifecycle. The aim is to strengthen relationships with customer service and help maintain customers and drive revenue Development.
Between the various channels or points of touch, CRM systems compile customer data between the client and the business, including the company's website, telephone, live chat, direct mail, social networks, and marketing materials. Detailed information can also be given by customer relationship management systems on customers' personal information, buying history, buying preferences, and customer-facing staff members' concerns.
The goal of Customer Relationship Management Software CRM is straightforward: strengthening customer relationships. CRM software helps businesses remain linked to consumers, streamline operations, and increase efficiency. They generally refer to a CRM system when people speak about Customer Relationship Management software (CRM), Which helps manage contacts, sales management, efficiency, and more.
Here in this article, we will discuss the below topics to explain CRM in a bit of detail. So, let’s get started!
- History of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
- Types of CRM System
- Importance of CRM to your company
- A CRM will give you an “All in one place” Experience.
- Impact of CRM on Satisfaction with Clients
- How can a CRM benefit its customers?
- With CRM, you'll never miss out on anything
- CRM Features & Integrations
- How CRM Facilitates Your Company Today?
- CRM Examples
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software History
The early 1970s The notion of customer relationship management began. Businesses had to rely on independent mainframe systems to automate sales at that time.
1982 The concept of Database marketing, namely applying statistical methods to analyze and gather customer data.
1986 A customer evaluation system released ACT called! Centered on the concept of digital Rolodex, which provided the service of contact management for the first time.
1993 Tom Siebel, who designed the first CRM product Siebel Systems Oracle, SAP, Peoplesoft, and Navision have begun to expand their sales, delivery, and customer support capabilities with embedded CRM modules to compete with these new and rapidly rising stand-alone CRM solutions.
1997 Customer relationship management was popularized due to the work of Siebel, Gartner, and IBM.
1997-2000 Leading CRM products were enriched with shipping and marketing capabilities.
2004 The first open-source CRM system was developed by SugarCRM
2009 Developers The options to take advantage of social media momentum started to be discussed, and resources were built to help businesses become available on all users' favorite networks.
November 2016 Forrester released a report where it "identified the nine most significant CRM suites from eight prominent vendors."
Types of CRM
CRM is a broad concept encompassing many aspects and types. Some of the primary forms of Customer Relationship Management Software are:
-
Strategic
Strategic CRM is focused on creating a customer-centric corporate culture. A company's focus is on being customer-centric and developing and executing its CRM strategy.
-
Operational
Operational CRM's primary objective is to provide a dashboard that offers an aggregate view of the three roles in a single customer view. A single page for each customer a business may have.
The dashboard can include customer statistics, past sales, previous marketing activities, and more, summarizing all customer-company relationships. Operational CRM consists of 3 main components: automation of sales forces, automation of marketing, and operation automation.
-
Analytical
The role of analytical CRM systems is to evaluate and present customer data obtained from various sources to allow company executives to make more informed decisions. Analytical CRM systems use techniques to analyze customer data, such as data mining, correlation, and pattern recognition.
-
Collaborative
The third primary goal of CRM systems is to integrate and exchange customer information through groups/departments and organizations with external stakeholders such as retailers, suppliers, and distributors. Feedback can be obtained via service calls to clients.
-
Customer Data Platform
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a computer system used by marketing departments that integrates data from multiple sources on individual customers into a single database with which other software systems can communicate.
Here's why your company matters with CRM?
Gartner estimates that customer relationship management (CRM) will be the single most significant revenue region for enterprise software spending by 2021. You know that you need a plan for the future if your company is going to last.
You have revenue, market goals, and profitability objectives. But it can be tricky to get up-to-date, accurate data on your success. How can you convert into valuable business knowledge the various data streams coming in from sales, customer care, marketing, and social media monitoring?
A CRM will give you an “All in one place” Experience
A simple, interactive dashboard that can tell you the history of a customer, the status of their orders, any unresolved problems with customer service, and more.
You can also opt to include their public social media activity details, likes, and dislikes, what they say and post about you or your rivals. To better understand the pipeline of orders or opportunities coming in, marketers may use a CRM solution, making forecasting more straightforward and precise.
From HR to customer care and supply chain management, some of the most significant efficiency gains will come from going beyond CRM as a sales and marketing tool and embedding it in your company.
Customer support teams find significant advantages in using them, while CRM systems have historically been used as sales and marketing tools. A CRM platform helps you handle the query across platforms without losing track and offers the client a single view of revenue, operation, and marketing.
Impact of CRM on Satisfaction with Clients
Since it can improve consumer loyalty and consumption behaviour and minimize customer feedback and the risk of customer defection, customer satisfaction has significant consequences for the economic performance of businesses.
For several different factors, introducing a CRM strategy is likely to affect consumer satisfaction and customer awareness.
- Firstly, for each customer, companies can tailor their offerings. CRM applications help companies customize their offerings to fit their customers' particular preferences.
- Secondly, CRM applications often enable businesses to process customer orders and requests quickly and precisely and manage customer accounts regularly.
- Also, CRM technologies help organizations handle customer relationships more efficiently through the phases of initiation, maintenance, and termination of relationships.
How does CRM give benefits to customers?
With Customer Relationship Management Systems, the day-to-day operation suits clients better. The three forms of equity, which are partnership, value, and brand, and essentially customer equity, are hypothetically related to these core eight advantages of CRM.
- Strengthened capacity to target successful clients.
- Integrated cross-channel assistance.
- Enhanced Productivity and profitability of the sales force.
- Enhanced pricing.
- Products and services that are personalized.
- Enhanced quality and efficacy of customer service.
- Campaigns are also called individualized marketing messages.
- Link on a common forum for clients and all platforms.
Research has found that a 5 percent increase in consumer retention raises customer lifetime earnings on average by 50 percent across various sectors and a rise of up to 90 percent in particular industries such as insurance.
No CRM will Lower Your Organization
For anything else, more administration means less time. An active sales team can generate a flood of data. Reps are out talking to clients, meeting customers, and seeking useful information on the route; this detail is all too frequently stored in handwritten notes, laptops, or the salespeople's heads.
On various channels, including telephone, email, or social media, your customers can contact you, ask questions, follow up on orders, or contact you about a problem. Communications may be overlooked or lost in information flow without a standard forum for client interactions, leading to a slow or unsatisfactory answer.
Information can get lost, meetings are not immediately followed upon, and it can be a matter of guesswork rather than a systematic exercise based on facts to prioritize clients. And when the leading salesperson moves on, it can all be amplified. But it is not just sales without CRM that are struggling.
And if you gather all this knowledge effectively, you're faced with the task of making sense of it. Extracting intelligence can be challenging. It can be challenging to produce reports, and they can waste precious sales time.
Managers can lose sight of what their teams are up to, which suggests that at the right moment, they can not provide the proper assistance, although a lack of supervision can also result in the team's lack of responsibility.
CRM Elements
CRM software consolidates customer information at the most basic level and records it into a single CRM database so that business customers can access and handle it more easily.
Many extra functions have been applied to CRM systems over time to make them more useful. Some of these functions include documenting different customer interactions through email, phone, social media, or other channels; automating different workflow automation processes, such as tasks, calendars, and notifications, based on system capabilities; Providing managers with the ability to control performance and efficiency based on data recorded inside the system.
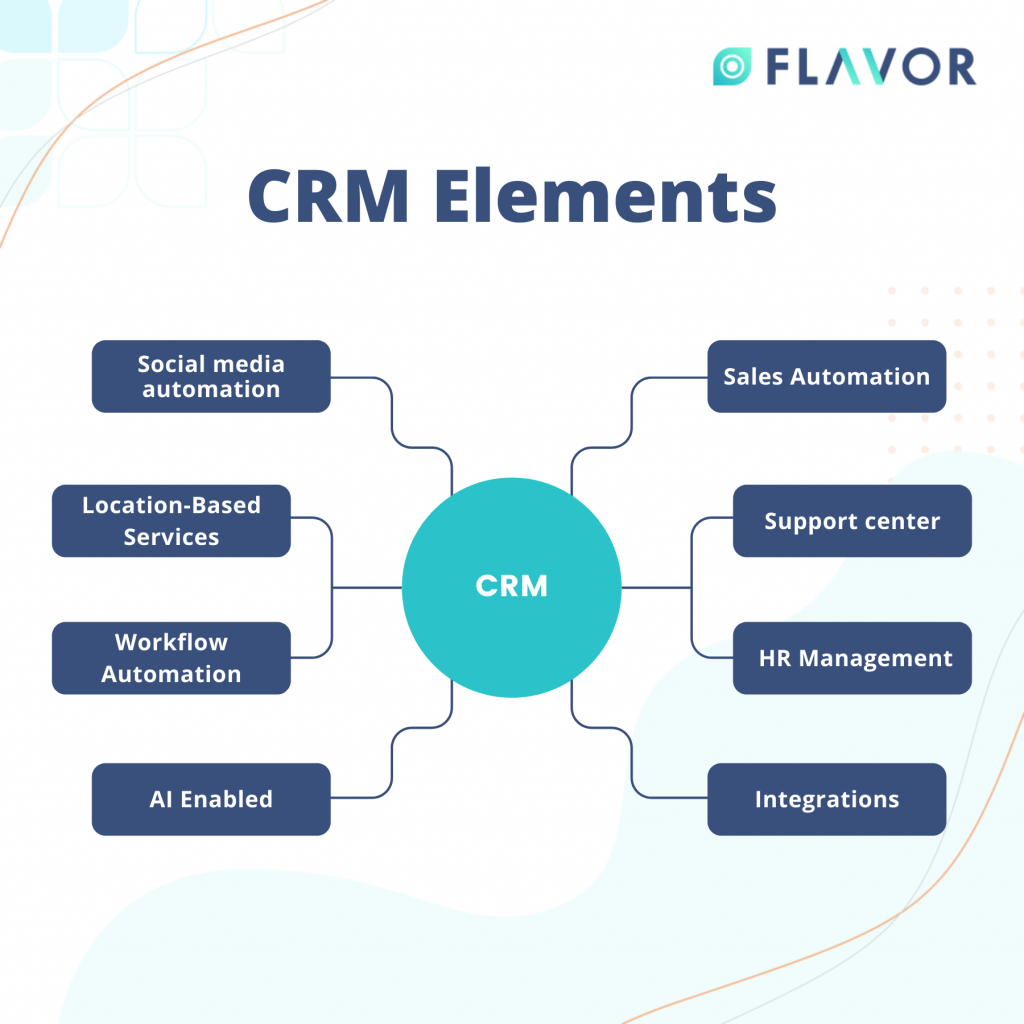
They Are Automating Ads
CRM software with marketing automation capabilities can automate routine activities at various points in the lead generation lifecycle to increase marketing efforts. For example, it might automatically submit email marketing content as sales prospects come into the system to convert a sales lead into a full-fledged customer.
Automation Salesforce
Tools for sales force automation control customer experiences and automate certain sales cycle business functions required to pursue leads, attract new customers and create customer loyalty.
Automation Support Center
Customer user experiences can be improved by automated contact center tools, such as chatbots. Contact center automation, designed to eliminate repetitive aspects of a contact center agent's work, may include pre-recorded audio that helps solve issues for customers and disseminate details.
Location-Based Services
Some CRM systems provide technologies that can create geographic marketing strategies based on consumers’ physical locations, often combined with standard GPS (global positioning system) location-based apps.
Human Resource Management (HRM)
CRM systems help manage employee information within an organization, such as contact information, performance reviews, and benefits.
Automation of Workflow
By streamlining mundane workloads, CRM systems simplify processes, allowing workers to concentrate on creative and more high-level tasks.
Artificial Intelligence(AI) Role
To automate repetitive activities, recognize customer-buying trends to forecast potential customer preferences, and more, AI applications such as Salesforce Einstein have been integrated into CRM systems.
Management of tasks. Some CRM systems provide features that help users keep track of client project specifics, such as priorities, strategic alignment, procedures, risk management, and progress.
Integration of Other Applications
Many CRM systems, such as call center and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, can integrate with other applications.
How CRM Facilitates Your Company Today?
How customer relationship management (CRM) is impacting and facilitating businesses is a next-level game.
Allow The BOTTOM LINE Changes
It has been shown that implementing a CRM platform yields tangible results, including direct improvements to the bottom line. CRM apps have an established track record of growing:
- BY UP TO +30 percent LEAD CONVERSION
- SALES Of UP TO +30 %
- PRODUCTIVITY Revenues Of UP TO +35%
- SATISFACTION OF CUSTOMER BY UP TO +35%
- SPECTER DECISION-MAKING BY UP TO +38%
- REVENUE BY UP TO +25%
Define and Lead Categories
A CRM system framework can help you easily and quickly find and add fresh leads and accurately categorize them. Sales will prioritize the opportunities that will close deals by concentrating on the right leads. Marketing can identify information that requires more nurturing and prime them to become quality leads.
Sales and marketing will concentrate their attention and resources on the right customers with full, reliable, centrally held information about customers and prospects.
Increase Services to Current Customers
Cross-selling and upselling possibilities become apparent by knowing your clients better, allowing you the potential to attract new business from current customers.
You will also be able to keep the customers satisfied with better quality by better visibility. It is possible that happy clients will become repeat clients, and, according to some reports, repeat customers spend more, up to 33 percent more.
CRM & the Revolution of Cloud Computing
The transition to cloud computing has perhaps been the most critical recent advancement in CRM systems. Organizations worldwide agents are working on the advantages of shifting knowledge, software, and services into a safe online environment, free from the need to install software on hundreds or thousands of desktop PCs and mobile devices.
With cloud storage CRM system, Data is stored on an external, remote network that employees can access; SAAS is also referred to as (software as a service) or on-demand CRM. Any time, anywhere, there is an internet connection, often with installation and maintenance monitored by a third-party service provider. The quick, relatively simple deployment capabilities of the cloud appeal to businesses with limited technical expertise or resources.
For businesses using cloud-based systems, data protection is a primary concern since it does not physically monitor its data storage and management. If the cloud provider goes out of business or is bought by another company, it can damage or lose an organization’s data. Compatibility problems can also occur when data is initially transferred from an organization’s internal structure to the cloud.
Job across all locations
Cloud-based CRM systems, like Salesforce, ensure that every user, all the time, has the same details. So, after a meeting or work from anywhere, your sales force out on the road can check info, update it instantly. So, anyone who wants it, from the sales staff to the customer service representatives, has the same knowledge. Learn more about the importance of mobile CRM for your business.
Offers for Cloud-based CRM:
- Speedier Deployment
- Automatic upgrades to applications
- Scalability and cost-effectiveness
- The ability to function on any computer, from anywhere,
- Increased cooperation
Cost-effective Cloud CRM
CRM systems can be fast and straightforward to implement. Also, there is no special installation required for a cloud-based system, and there is no hardware to set up, keeping IT costs down and eliminating the hassle of version control and upgrade schedules. In terms of flexibility, cloud-CRM systems like Salesforce are also flexible-you don't pay for any features that are not useful to you.
Generally, the number of users who use the system and the kinds of functionality you need are priced on cloud-based CRM systems
In operation, CRM Examples
CRM for Social Media
In CRM, social media includes companies directly communicating with customers via social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. Social networking offers an interactive platform for consumers, whether they air complaints or endorse goods, to share interactions with a brand.
Social CRM brings value to businesses and clients through customer forums, where customers post product feedback and can communicate with other customers in real-time to troubleshoot problems or study products. For some types of issues, consumer groups may provide low-level customer support and reduce the contact center’s number of calls. Consumer communities can also generate new product ideas or suggestions that businesses can use in place of feedback groups.
Business-to-business (B2B) Activities
In a B2B environment, a CRM system helps track sales as they pass through the sales funnel, allowing a company to fix any problems during the process. In the B2B industry, CRM systems help build more insight into leads and, ultimately, improve productivity throughout the sales process.
Criticism
If there is no proper supervision, CRM systems can quickly become ineffective, and they are not correctly applied. The data sets must also be appropriately linked, distributed, and structured so that users can quickly and easily access the information they need. Research reports also indicate that consumers are increasingly unhappy with contact center experiences due to lags and wait times.
They often request and involve several communication channels with a corporation, and information must be transferred seamlessly by these channels. Therefore, delivering a cross-channel customer experience that can be both consistent and efficient is increasingly critical for businesses. The processing of consumer data, such as personally identifiable information, must strictly comply with customer privacy regulations, frequently requiring additional legal assistance expenses.
Part of the CRM paradox stems from the task of deciding precisely what CRM is and what it can do for a company. The paradox of CRM, also known as the dark side of CRM systems.'
So,
In short words, we can say what Customer Relationship Management CRM Software is: CRM systems work better when businesses spend time cleaning up their customer information to remove redundant and outdated records before supplementing external information sources with CRM data.

