Operations Management : Definition, Principles and Strategies

Operations management is the area of management concerned with designing and monitoring the production procedure and redesigning the business functions in producing goods and services. It includes ensuring that business functions efficiently use minimum resources and effectively meet consumer needs.
Table of Contents
- What is Operation Management?
- Principles of Operation Management
- Why is Operations Management crucial for modern organizations?
- Strategies of Modern Operations Management
- 5 Tips for Smooth Operation Management
What is Operation Management?
Operations management is the process of managing operations in a way that produces the highest possible value for an organization. It is a complex process involving understanding and implementing operations management principles. By understanding these principles, you can manage any type of operation effectively and ensure that processes are executed in a consistent and effective manner. This will ultimately lead to increased customer satisfaction. Operations management is a critical component of any business, and understanding the basics will help you to manage it effectively and efficiently.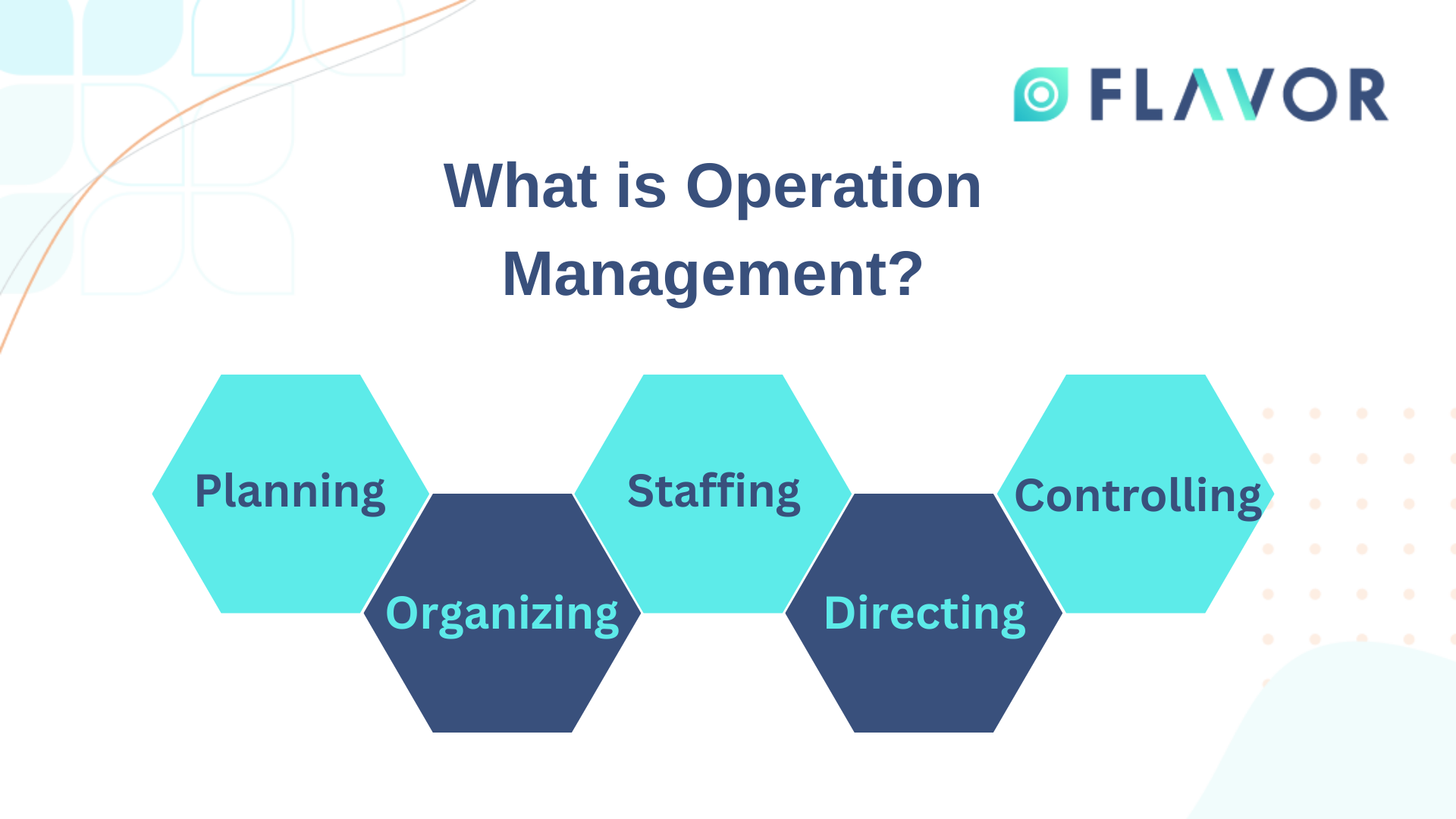
You must choose regulations from conventional business administration and practice them in your operations. These regulations are:
Planning: preparing and strategizing target-critical tasks with an organization.
Organizing: assembling and coordinating operations to optimize production efficiency.
Staffing: determining a particular skill profile to execute various operations.
Directing: guiding and executing the execution of various operations of a company.
Controlling: controlling subordination during the execution procedure.
Why is operations management important?
Operations management is essential to the success of any business. It helps ensure that products and services meet customer expectations and meet financial goals. operations management ensures quality products are produced on time, within budget, and comply with applicable regulations.
Operations management is an overarching process that integrates and coordinates the activities of different departments within a business in order to produce products or services that meet customer requirements. These operations include product development, production, supply chain management, accounting/finance, human resources management and marketing.
Operations management ensures quality products are produced on time with minimal interruption; meets financial goals; maintains efficient communication throughout the supply chain; complies with all applicable regulations while protecting workers & the environment and supports innovation and growth.
Practising operations management
Operations management is a field that deals with the management of resources and products to reach desired outcomes. It can be a challenging field, but with the right principles and strategies in place, you can make your business run more smoothly. Understandably, planning is a key aspect of operations management.
This includes forecasting future needs, scheduling resources to meet those needs, and ensuring that resources are effectively utilized. In addition, effective operations management includes systems management, which helps to maintain control over resources and data. It's also important to take into account safety considerations when managing operations. By working in operations management you'll be able to streamline your business and achieve desired outcomes more efficiently.
common tasks
Operations management is an important and integral part of any business. It helps to ensure that operations run smoothly, ensuring the production process runs effectively while meeting customer demands. To understand this complex field, it's helpful to first define its purpose. From there, learn about the principles and strategies involved in working within operations management departments. Finally, take a look at some practical exercises you can use in your day-to-day work!
Skills
Operations management is a field that requires good organisational skills. In order to be successful, you need to have an understanding of various operations strategies and how they can help your business achieve its objectives. You also need to be able to keep track of all the moving parts within the business in order to make informed decisions. This essential skill set will help you solve problems quickly and efficiently, ensuring that your business runs smoothly 24/7. If you're looking for a career change or want more control over your work life, then operations management may just be the right fit for you!
Principles of Operation Management
There are ten fundamental principles of operations management:
1. Accountability
Managers and supervisors are expected to set metrics and rules, regulate the duties of their subordinates, and frequently monitor whether the goals are achieved or not.
2. Causality
Even after giving their best efforts, problems still may arise in a few cases. The management’s responsibility is to find and understand the root cause of the issues, not worsen.
3. Change
Every employee in the company must learn to accept changes in the market. It involves understanding the customer, target audience, and what they want.
4. Fundamentals
Operations managers must understand how to comply with fundamentals because it is the key to the production's success. It is crucial to ensure the accuracy of BOMs, inventory data, and other general tasks to acquire desired results.
5. Humility
No one enjoys working with an aggressive person who has a know-it-all attitude. Operations managers need to stay humble like ordinary people who don’t know everything about everything.
6. Managed Passion
Employee morale is one of the primary drivers of a company’s growth. Therefore, operations managers must have the ability to inspire their employees or subordinates to be passionate about their work.
7. Organization
In manufacturing, the processes are interconnected. Therefore, all the components must be consistent and predictable to acquire the same revenue in all outcomes.
8. Reality
Operations managers must be realistic and concentrate on problems rather than techniques, as no equipment offers global solutions.
9. Success
Managers must clearly describe what they consider successful so that the workforce has the parameters to work with to acquire targets.
10. Variance
The variance of techniques must be encouraged because differences can be a seed of creativity if controlled well.
Why is Operations Management crucial for modern organizations?
Now that you know the basics and principles of operation management let us explore the importance of operations management for modern organizations.
- Better positioning: A robust operations system can become a true competitive benefit.
- Better products and services: You will manufacture better products and services with transparent operations and processes.
- Improved collaboration: transparent processes stimulate cross-team collaboration.
- Increased revenue: decreasing costs and enhancing your services will generate higher revenue for your business.
- Overall improvements: at the end, acquiring operational excellence will enhance your overall performance.
- Regulatory compliance: stating clear guidelines, policies, and rules will assist your team to be more accountable and compliant.
Strategies of Modern Operations Management
1. Leveraging Data
Operations managers rely on accurate, quality, and reliable data for strategic marketing and decision-making. Two types of commonly used data analysis methods are effectiveness and efficiency metrics.
2. Controlling Data Challenges
Data is often vast, so the result varies, making it tough to analogize. Luckily, with the help of advanced software and systems, operations managers can see, control, and examine data with ease and in an organized manner.
3. Analyzing Inventory
The inventory can be easily analyzed if an organization has inventory management software installed and in use. This software will also make it simpler for operations managers to categorize lists.
4. Designing Process
Operations managers work intensely to produce the best research, generate accurate estimates, and the ideal development of goods procedure. All this hard work eventually results in a long-lasting impact.
5. Forecasting and Setting Goals
Defining goals and forecasting help the company achieves its goals. Forecasting needs complete and precise historical data. With the use of ERP software, the task can be done quickly.
6. Collaboration Between Departments
Collaboration between departments is necessary so that the human resource, finance, sales, and marketing teams can work together to make progress for the organization. AN ERP software makes collaboration between departments easier by providing centralized information for every department.
7. Social Responsibility
The main concerns a company must take care of are the environment's responsibilities and the communities directly impacted by the business. It is particularly true for manufacturing companies that deal with solid and liquid waste problems.
8. HR Management
Managing employees is crucial for every company since the workforce is the backbone of an organization. Without a crew, everyday business operations will terminate, and your organization will not be able to create goods or services.
5 Tips for Smooth Operation Management
- The operations manager must be skilled at what they do and must be a good leader.
- The operations manager must inspire and set an excellent example for their subordinates.
- Operations managers must be very accurate with the data because they are responsible for preparing, estimating, and examining the various features associated with production.
- The operations manager can use ERP systems to generate real-time and accurate data linked to inventory, production, and sales.
- ERP system also allows inter-departmental incorporation so that employees from different departments and locations can cooperate via the same system.
Key Takeaway
The key takeaways of this article are:
- Operations are one of the vital strategic functions of any organization.
- Operations management aims to produce maximum goods and services to meet the customers’ requirements with minimum resources available.
- Operations decisions involve planned decisions that have a long-term impact and frequently include significant expense and resource commitments.

